|
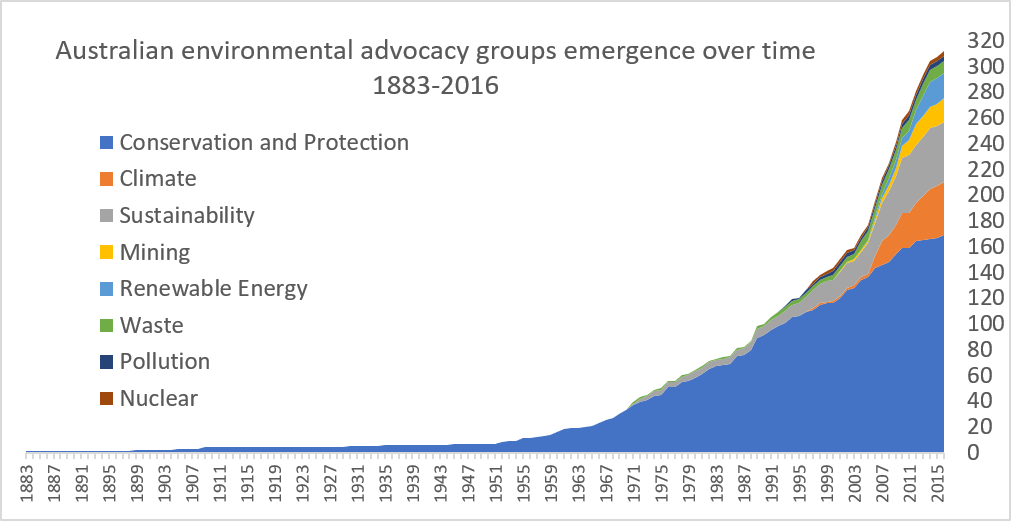
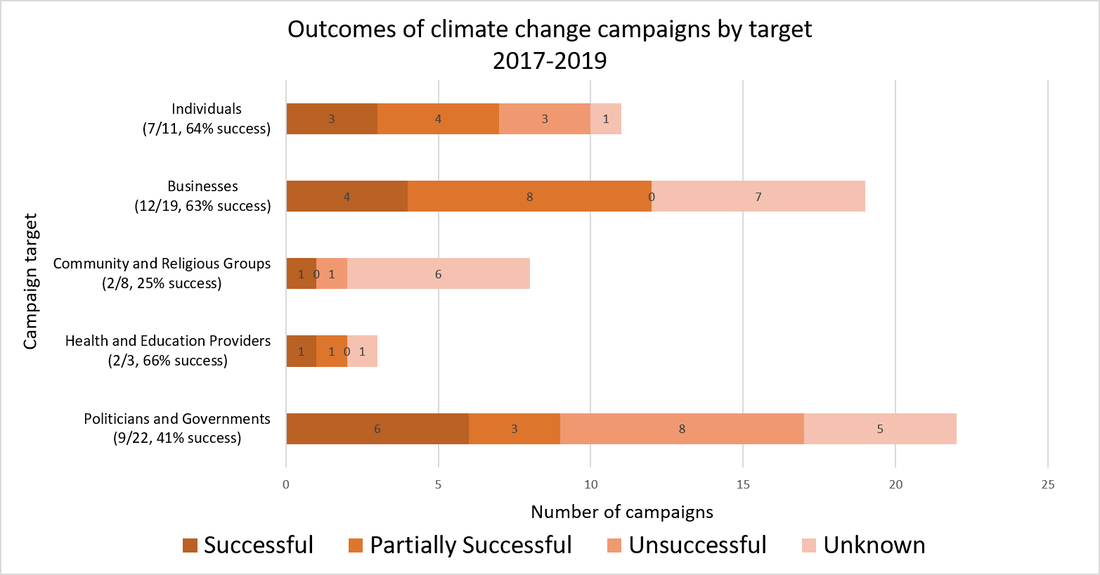
Every day most of us reap the benefits of collective action undertaken in the past by others. Momentous upheavals play out over centuries as the rights of some and duties of others change in tempo with changing norms and laws. We have seen this play out through history as legal slavery is abolished, disability rights are protected, and demands for Indigenous sovereignty grow. These changes ebb and flow at the macro level, the viewpoint we use to understand changes in society at large. But how do we know what the actual forces of social change are? We must understand the meso-level dynamics of groups, communities and institutions, or investigate even deeper into the micro-level influences on social change fueled by individuals and their activities. Delving into this micro world of activism is how I spent the first year of my PhD. New technologies have enabled digital humanities researchers to gather large empirical databases to investigate the characteristics of social change at the group and individual level. I used these technologies to capture what environmental movement groups and their members are doing, where they are doing it, and what they are achieving. Our findings have been published in two journal articles. Our first paper published in Environmental Communication - The Characteristics, Activities and Goals of Environmental Organizations Engaged in Advocacy Within the Australian Environmental Movement - uses data captured through a content analysis of 497 websites to show how active environmental advocates are. With over 900 campaigns and thousands of online and offline events, they have been busy advocating for environmental care for more than a hundred years. Furthermore, most of their efforts are not radical, with activists predominantly working as volunteers in our local communities with the aim to increase awareness and understanding about more pro-environmental behaviors. But activity is one thing; outcomes are another. We wanted to know whether this activity is successfully effecting change. To investigate, we went back to the micro level to ascertain the outcomes of climate change campaigns. The causes of climate change are intractable, diffuse, and woven into the fabric of our social, political and economic systems. So how do activist groups try to stop climate change, and is any one way more successful than the others? Our findings were published in the paper ‘Understanding the outcomes of climate change campaigns in the Australian environmental movement’ in the journal Case Studies in the Environment. We identified the target and goal of 58 campaigns specifically focusing on climate change and tracked their outcomes over a 2-year period. Some of these campaigns aimed to stop new coal mines. Some of them wanted government to enact new climate policies. Our data showed that almost half of these campaigns either fully or partially achieved their goal. For example, coal mines were delayed, and climate policy was enacted. In particular, 63% of campaigns asking individuals, businesses and health and education providers to reduce their climate impact were either partially or fully successful. In total 49% of all campaigns achieved full or partial success. These campaigns each only focus on one small piece of the solution to climate change and we cannot be sure how much campaign activities directly influence outcomes. Yet our research using real-world data shows that these environmental groups are connected to, and likely playing a crucial role in driving meaningful change which will help protect the environment. These activities constitute the incremental successes and failures which together drive social change. - By Robyn Gulliver
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorsAll researchers in the Social Change Lab contribute to the "Do Good" blog. Click the author's name at the bottom of any post to learn more about their research or get in touch. Categories
All
Archive
July 2024
|
Social Change Lab
Join our mailing list!Click the button below to join our mailing list:
Social Change Lab supports crowdfunding of the research and support for the team! To donate to the lab, please click the button below! (Tax deductible receipts are provided via UQ’s secure donation website.) If you’d like to fund a specific project or student internship, you can also reach out directly!
|
LocationSocial Change Lab
School of Psychology McElwain Building The University of Queensland St Lucia, QLD 4072 Australia |
Check out our Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2017
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
